In the world of long-term investing, few strategies are as enduring as the one championed by legendary fund manager Peter Lynch. His method, often called Growth at a Reasonable Price (GARP), focuses on finding companies with good, lasting earnings growth that are not overpriced by the market. The central idea is to invest in businesses that are easy to understand, have sound finances, manageable debt, and a clear way to keep growing, all while steering clear of the excitement around overly fast growth that cannot last. By using a disciplined set of fundamental filters, investors can look for companies that fit this careful, long-term thinking.
One company that currently appears from such a look is Baker Hughes Co (NASDAQ:BKR), a global energy technology firm. As a provider of oilfield services, equipment, and industrial energy solutions, BKR works in a sector that is both vital and intricate. For an investor using Lynch’s ideas, the main question is if this company’s financial profile fits the requirements for lasting growth at a fair price.
Fit with Peter Lynch Criteria
A Peter Lynch-inspired look usually searches for a particular mix of profitability, financial soundness, and price. Baker Hughes seems to satisfy many of these important measures, which are made to find companies with lasting competitive strengths and management that treats shareholders well.
- Lasting Earnings Growth: Lynch preferred companies with a shown history of earnings growth, but was cautious of extreme growth that could mean uncertainty. Baker Hughes shows a 5-year average Earnings Per Share (EPS) growth rate of 23.35%, which is solid. More significantly, this number is within the often-mentioned Lynch range of being above 15% but below 30%, hinting at a speed that could be more maintainable than very fast increases.
- Fair Price Compared to Growth: This is the foundation of the GARP method, calculated by the PEG ratio (Price/Earnings to Growth). A PEG ratio at or below 1 hints the stock’s price could be fair compared to its earnings growth. Baker Hughes has a PEG ratio (using past 5-year growth) of 0.88, showing the market may not be paying too much for its past growth path.
- Good Profitability: Lynch sought companies that effectively create profits from shareholder equity. Baker Hughes’ Return on Equity (ROE) of 15.92% easily goes beyond the 15% level often linked to high-quality, profitable companies.
- Sound Financial Health: To make sure of strength, Lynch stressed careful balance sheets. Baker Hughes reports a Debt-to-Equity ratio of 0.33, which is not only under the look’s usual limit of 0.6 but also matches Lynch’s own liking for a ratio below 0.25. This points to a capital structure using more equity than debt. Also, its Current Ratio of 1.41 shows it has enough short-term assets to meet its near-term obligations, passing another basic financial health test.
Fundamental Health Review
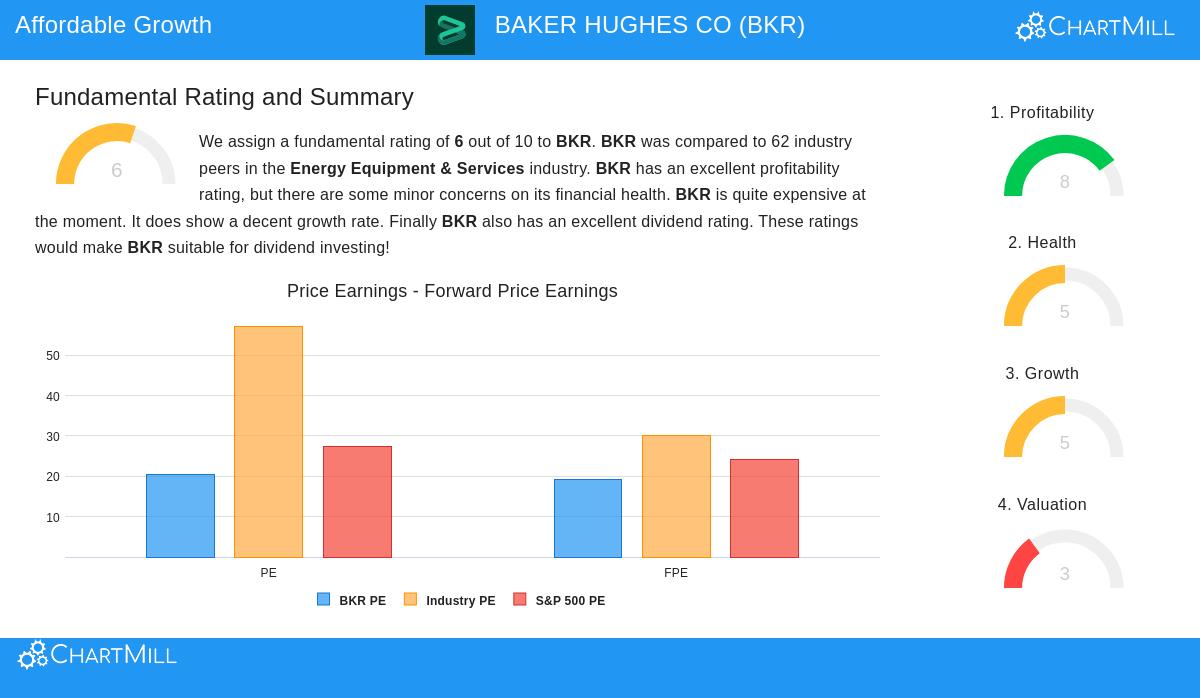
Beyond the specific look measures, a wider view of the company’s fundamental rating gives background. According to a detailed fundamental analysis report, Baker Hughes shows a varied but mostly good picture, scoring 6 out of 10 overall compared to others in the Energy Equipment & Services industry.
The company’s clear strength is its profitability, where it scores an 8 out of 10. It has industry-leading numbers in Return on Assets, Return on Invested Capital (ROIC), and profit margins, all of which have gotten better in recent years. Its dividend profile is also good, with a steady long-term payment history and a maintainable payout ratio, scoring a 7.
Points to think about include its financial health, which scores an average 5. While its stability numbers like Debt-to-Equity are good, its liquidity ratios (Current and Quick Ratio) are not as strong as many industry peers. The main area of discussion is price, which scores a 3. The report states the stock looks "rather expensively" priced on some absolute measures, though it costs less than many industry peers and the wider S&P 500 on a P/E basis. This highlights the value of the PEG ratio, which accounts for the company’s good growth and makes the price seem more fair.
A Stock for the Long-Term Portfolio?
For an investor following the Peter Lynch method, Baker Hughes is an interesting example. It works in the vital, if occasionally up-and-down, energy sector—an area Lynch might call "dull" but understandable. The company meets important number-based filters centered on lasting growth, profitability, and balance sheet care. Its below-1 PEG ratio is a key number, suggesting its higher price is supported by its growth past.
However, Lynch’s strategy was never about automatic looking. It required knowing the business. Investors must think about the company’s future in the shift in energy, its competitive place against others, and if its expected growth can persist. The fundamental report indicates future EPS growth is forecast to be positive but at a more measured speed than the past five years.
Interested in finding other companies that fit this disciplined method? You can see the current results of the Peter Lynch strategy look here.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice, an endorsement, or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any security. Investing involves risk, including the potential loss of principal. Always conduct your own due diligence and consider consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.




