
3 Diversified Sector-Based Portfolios

These 3 example portfolios are designed to provide a mix of growth potential and stability by investing in different sectors.
Example 1: Balanced Growth and Stability Portfolio
Sector Allocation:
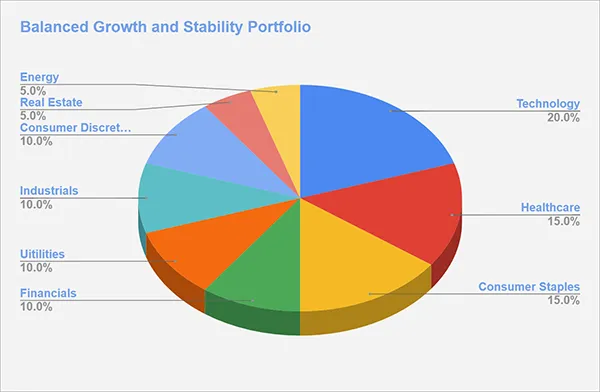
Technology (20%): Focus on growth-oriented tech companies with high innovation potential.
Healthcare (15%): Invest in established healthcare companies that provide consistent returns and stability.
Consumer Staples (15%): Include companies that offer essential goods and services, providing a safety net during economic downturns.
Financials (10%): Focus on banks, insurance companies, and investment firms, which tend to perform well during economic expansions.
Utilities (10%): Invest in utility companies that provide steady, reliable returns with low volatility.
Industrials (10%): Focus on manufacturing and infrastructure companies that benefit from economic growth.
Consumer Discretionary (10%): Include companies in the retail, automotive, and leisure sectors that thrive in growing economies.
Real Estate (5%): Invest in REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) to gain exposure to property markets, offering both income and potential capital appreciation.
Energy (5%): Include companies in the oil, gas, and renewable energy sectors, balancing growth potential with sector volatility.
Strategy:
Risk Management: This portfolio balances higher-risk, higher-reward sectors (like technology and consumer discretionary) with more stable, defensive sectors (like consumer staples and utilities).
Return Potential: The allocation to growth sectors provides strong potential for capital appreciation, while defensive sectors offer stability and income.
Example 2: Conservative Income and Stability Portfolio
Sector Allocation:
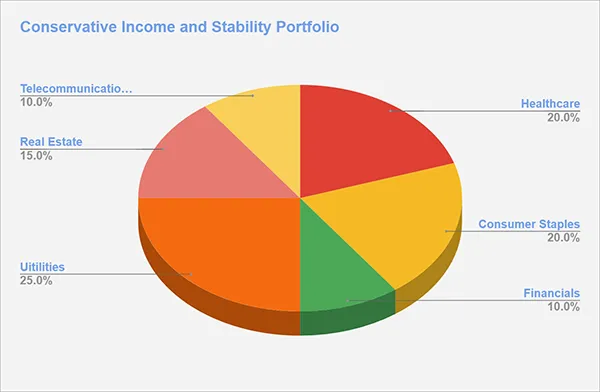
Utilities (25%): High allocation to utility companies for their stable, dividend-paying characteristics.
Healthcare (20%): Focus on large-cap healthcare companies with consistent earnings and reliable dividends.
Consumer Staples (20%): Invest in companies that provide essential goods, ensuring steady performance regardless of economic conditions.
Real Estate (15%): REITs provide income through dividends and potential for long-term capital appreciation.
Financials (10%): Conservative allocation to stable, dividend-paying financial institutions.
Telecommunications (10%): Include companies that offer reliable, high-yield dividends and operate in a less volatile sector.
Strategy:
Risk Management: This portfolio prioritizes low-volatility, income-generating sectors, making it suitable for risk-averse investors.
Return Potential: The focus is on preserving capital and generating steady income through dividends, rather than aggressive growth.
Example 3: Aggressive Growth Portfolio
Sector Allocation:
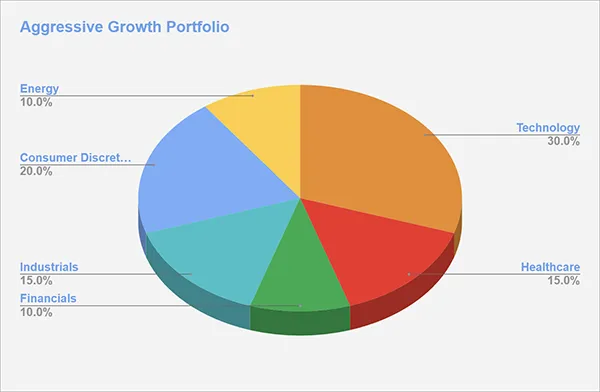
Technology (30%): Heavy emphasis on tech stocks, particularly in emerging areas like AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
Consumer Discretionary (20%): Focus on companies in the e-commerce, luxury goods, and entertainment sectors that have high growth potential.
Healthcare (15%): Target biotech and pharmaceutical companies with strong R&D pipelines and growth prospects.
Industrials (15%): Invest in companies poised to benefit from infrastructure spending and technological advancements.
Financials (10%): Select financial tech companies and investment firms with strong growth potential.
Energy (10%): Include renewable energy companies with long-term growth prospects.
Strategy:
Risk Management: While this portfolio is growth-oriented and higher-risk, it still includes some diversification across sectors to mitigate potential losses.
Return Potential: The focus is on sectors with the highest potential for rapid growth, accepting higher volatility for the possibility of substantial returns.
Conclusion:
These three example portfolios - Balanced Growth and Stability, Conservative Income and Stability, and Aggressive Growth - demonstrate how sector-based allocation can be tailored to different investment goals and risk tolerances.
- The Balanced Growth and Stability portfolio offers a middle ground, combining growth potential with defensive sectors for stability.
- The Conservative Income and Stability portfolio focuses on lower-risk sectors that provide steady income, suitable for risk-averse investors.
- The Aggressive Growth portfolio heavily weights high-potential sectors for investors seeking maximum growth, albeit with higher risk.
Each portfolio showcases how sector diversification can be strategically employed to manage risk while pursuing specific financial objectives. The key takeaway is that there's no one-size-fits-all approach to sector allocation. Instead, investors should consider their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon when constructing their portfolios.
Remember, regular review and rebalancing are crucial to maintaining the desired sector mix as market conditions change over time!
Ultimately, sector-based portfolio construction is a powerful tool for tailoring investments to personal financial strategies, potentially leading to more effective risk management and goal achievement in the long run.







